
If the anticodon does not match the codon, base pairing cannot happen and the tRNA is rejected. If the anticodon of the new tRNA matches the mRNA codon, base pairing occurs and the two amino acids are linked by the ribosome through a peptide bond. Elongationįollowing initiation, a new tRNA-amino acid complex enters the codon next to the AUG codon. The resulting large complex forms a complete ribosome and initiates protein synthesis. The initiator tRNA which is equipped with the anticodon (UAC) also binds to the start codon (AUG) of the mRNA. These steps are briefly discussed below: Initiation There are three major steps in translation: initiation, elongation, and termination. Each amino acid has a unique synthetase and the active site of each enzyme fits only one specific combination of the amino acid and tRNA. These are enzymes that link each amino acid to their corresponding tRNA with the help of a two-step process. tRNA carry a particular amino acid, which is added to the growing polypeptide chain if complimentary codons bond. Each tRNA is read as a ribonucleotide triplet called an anticodon that is complementary to an mRNA codon. This is a single strand of RNA composed of approximately 80 ribonucleotides. MRNA must interact with ribosomal RNA (rRNA), the central component of ribosomal machinery that recognizes the start and stop codons of mRNA, and tRNA, which provides the amino acid once bound with a complimentary mRNA codon. Strands of mRNA are made up of codons, each of which signifies a particular amino acid to be added to the polypeptide in a certain order. It is a single strand molecule, complimentary to the DNA template, and is generated through transcription. MRNA is used to convey information from DNA to the ribosome. Upon reaching the stop codon, the ribosome ceases translation and releases the mRNA and newly generated polypeptide. The mRNA possesses a stop codon, a sequence of three nucleotides that indicates that translation is complete. The ribosome moves along the single strand mRNA, and when a complimentary codon sequence belonging to amino acid bearing tRNA bonds with the mRNA, the amino acid is added to the chain. The nucleotide sequence in mRNA is recognized in triplets, called codons. It provides the enzymes needed for peptide bond formation. The ribosome is a complex organelle, present in the cytoplasm, which serves as the site of action for protein synthesis.


These four structures are briefly explained below: Ribosome The key components required for translation are mRNA, tRNA, ribosomes, and aminoacyl tRNA synthetases.
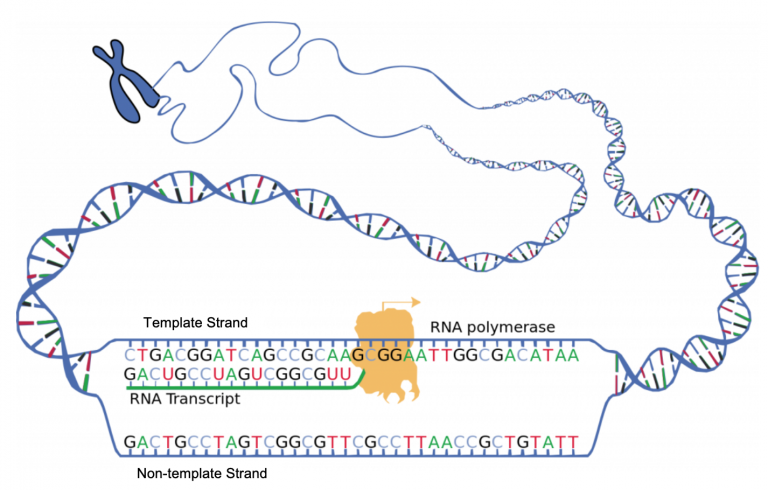
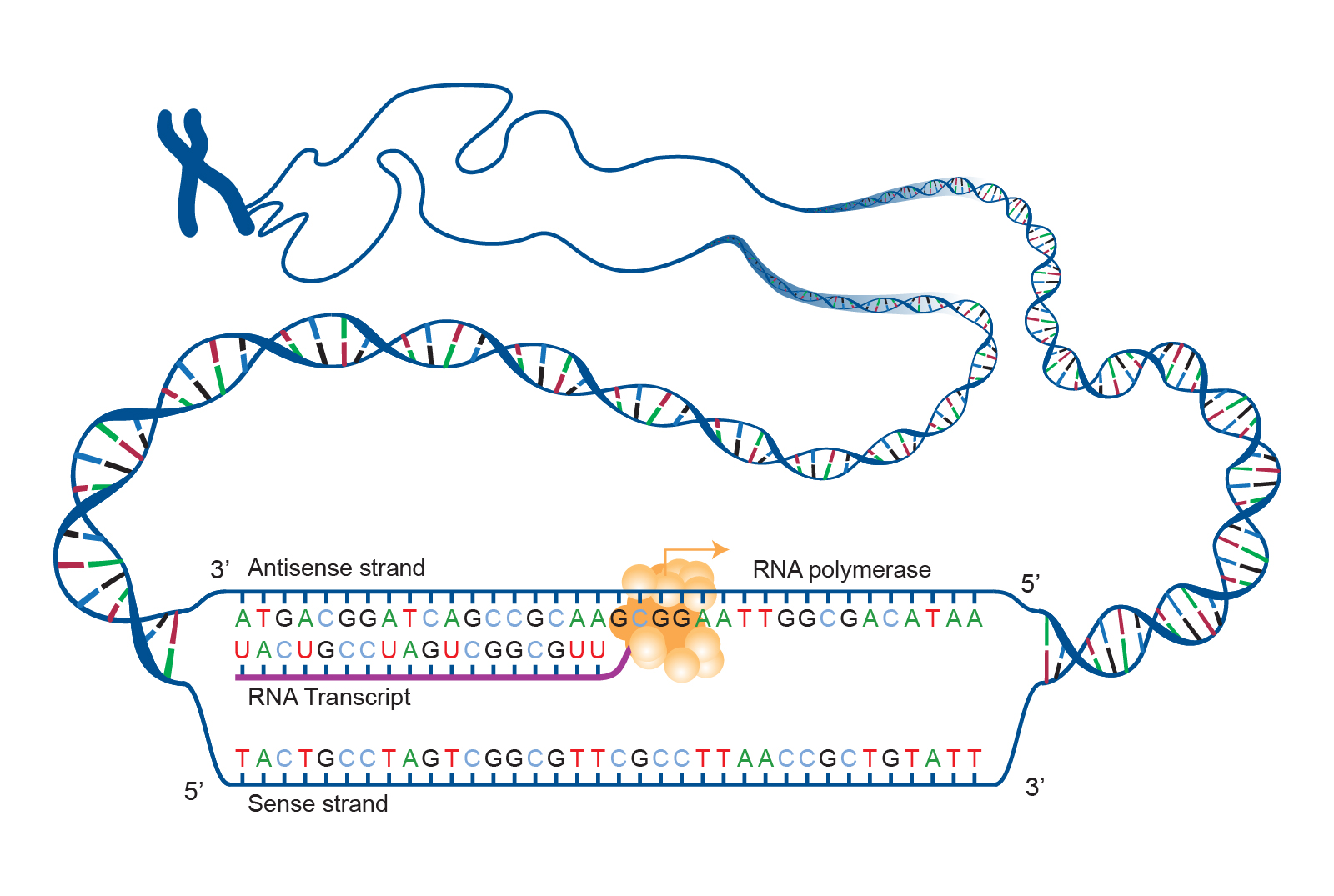
Cellular components involved in DNA translation Folding of the polypeptide creates an active protein, able to perform functions within the cell. In this process, the mRNA is decoded to produce a specific amino acid chain, known as a polypeptide. TRNAs carry particular amino acids, which are linked together by the ribosome. Ribosomes facilitate translation in the cytoplasm, by inducing the binding of complimentary transfer RNA (tRNA) anticodon sequences to the mRNA. Single stranded mRNA then acts as a template during translation. The genetic information in DNA is used as a basis to create messenger RNA (mRNA) by transcription. Image Credit: nobeastsofierce / Shutterstock Reviewed by Michael Greenwood, M.Sc.ĭNA translation is the term used to describe the process of protein synthesis by ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
